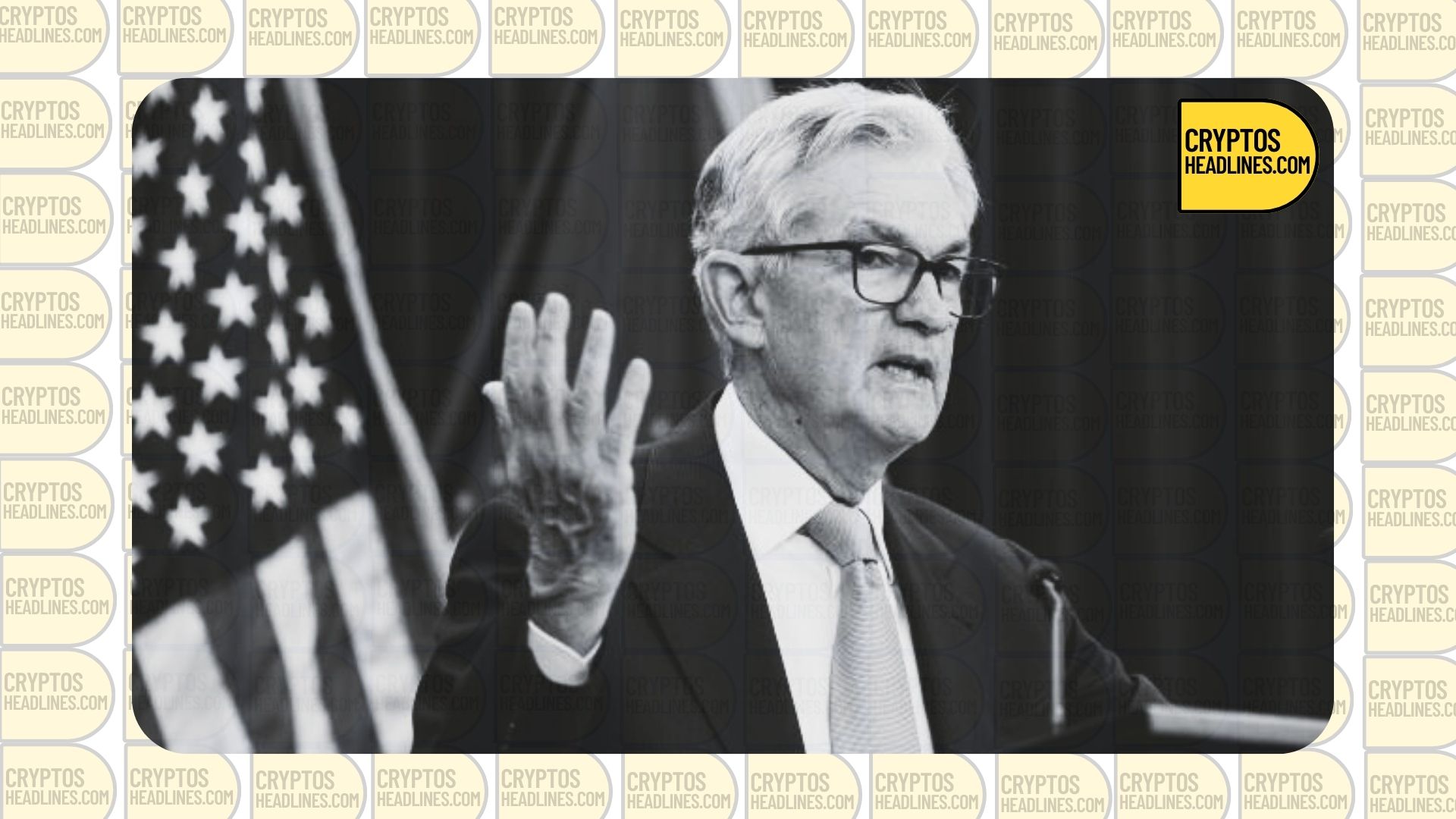
The Federal Reserve increased the federal funds rate by a small amount (25 basis points) on Wednesday. This means the rate is now between 5% and 5.25%. This is the first time the rate has been this high since 2007.
The increase of 25 basis points in the federal funds rate was not a surprise to many, but it happened at a time when some banks had recently collapsed. JPMorgan had to buy First Republic after regulators took it over, while regulators seized Silicon Valley Bank after its CEO’s comments caused a panic among depositors. Signature Bank was also taken over by regulators shortly after, and in March, Silvergate, which had a lot of exposure to cryptocurrency, voluntarily closed down.
The Federal Reserve did not include any wording that indicated there would be more rate hikes in the future, which suggests they may pause for now. The Fed will continue to watch and evaluate new information, and decide whether it’s necessary to make any more changes to monetary policy in the future.
Back in March, Powell said that it was still too early to completely understand the impact of the banking crisis. In the recent decision made in May, the Federal Reserve repeated its belief that the banking system is strong and can withstand challenges.
Powell is scheduled to speak at 2:30 pm Eastern Time in a press conference, where he will probably be asked about the Federal Reserve’s view on the banking industry after the takeover of First Republic.
If the Federal Reserve begins to lower interest rates by the end of 2023, the market has probably already anticipated this move, and the Fed will likely be able to avoid any negative impact on the financial markets. However, if the Fed deviates from this plan, there is a higher risk of a recession or prolonged high inflation, which could lead to a drop in the market. This was stated in an email by Ruslan Lienkha, the chief of markets at YouHodler.
Back in March, Powell repeated his belief that it was possible to have a “soft landing”, which means controlling inflation without causing a crisis or recession. He has been using this term since the Federal Reserve began raising interest rates.
Although inflation has started to slow down a bit, it still remains at a high level. According to the consumer price index, prices increased by 5% during the 12 months ending in March, which is slightly lower than the 6% reported in February.
The Federal Reserve aims to achieve a 2% target rate for inflation, which is also the target rate for the fed funds rate.
According to Greg Magadini, who is the director of derivatives at a crypto analytics company, Bitcoin’s performance this year is influenced by macro events. A 25 basis point hike in rates has already been factored into the market, so there should not be much of an impact there. If the Federal Reserve gives guidance that it will pause rate hikes in the future, it could be good news for Bitcoin, and it could increase slightly in value to around $29,000-$30,000. However, without any surprises, it’s unlikely that Bitcoin will significantly surpass the $30,000 mark.
A look at how stocks, bonds and Bitcoin have performed since rate hikes began
Something I pointed out to @eToroUS clients: $BTC has led the stock market in seven out of the last 10 Fed days 💥 pic.twitter.com/QMMozvieZO
— Callie Cox (@callieabost) May 3, 2023